All about Business Analyst Role | Frequently asked Questions
A business analyst is a professional who analyzes an organization or business domain (real or hypothetical) and documents its business, processes, and systems. Business analysts use data to understand business processes, identify problems, and work with cross-functional teams to develop solutions. This article covers All about Business Analyst Role | Frequently Asked Questions.
Business Analyst Basics
Business analyst roles and responsibilities
Here are some specific responsibilities that may be included in a business analyst job description:
- Gather and analyze data to understand business processes and identify problems
- Document business requirements and functional requirements
- Work with cross-functional teams to develop and implement solutions
- Facilitate workshops and interviews with stakeholders to gather requirements
- Use data analysis and visualization tools to understand and communicate data
- Create process maps and other documentation to document business processes
- Test solutions to ensure that they meet business requirements
- Communicate findings and recommendations to stakeholders
- Continuously seek to improve business processes and identify new opportunities for growth
Overall, the role of a business analyst is to use analytical and technical skills to help organizations understand and solve business problems.
Business analyst for beginners
If you are starting out in a career as a business analyst, there are a few key things you should know:
- Business analysis is a broad field: Business analysts work in a wide range of industries, including finance, healthcare, technology, and manufacturing. As a business analyst, you may work on a variety of projects in different sectors, so it’s important to be open to new challenges and to be willing to learn.
- Communication is vital: Business analysts work with various stakeholders, including executives, managers, and subject matter experts. Strong communication skills are essential for building relationships and getting buy-in for your recommendations.
- Data is your friend: Business analysts use data to understand business processes and identify problems. It’s important to be comfortable working with data and to have strong analytical skills.
- Documentation is important: Business analysts create various documents, including business requirements documents, functional requirements documents, and process maps. It’s important to be able to document requirements and solutions in a clear and concise manner.
- Don’t be afraid to ask questions: As a business analyst, you will be working on projects that are new to you. It’s important to ask questions and seek out information and resources to help you understand the business and the project you are working on.
How business analysts work
Business analysts often work on various projects and may be involved in different stages of the project lifecycle, from planning and analysis to implementation and evaluation. They may also work with various stakeholders, including executives, managers, and subject matter experts. They may be involved in both technical and non-technical aspects of a project.
How business analysts gather requirements
Gathering requirements is an important part of the business analysis process. It involves working with stakeholders to understand their needs and expectations and documenting those needs in a clear and concise manner.
There are several techniques that business analysts can use to gather requirements, including:
- Interviews: Business analysts can conduct interviews with stakeholders to understand their needs and expectations in more detail. Interviews can be conducted one-on-one or in groups and can be structured or unstructured depending on the project’s needs.
- Workshops: Business analysts can facilitate workshops with stakeholders to gather requirements and ideas. Workshops can be used to identify the needs of different stakeholder groups, prioritize requirements, and brainstorm solutions.
- Prototyping: Business analysts can use prototyping to gather requirements and test ideas with stakeholders. Prototyping involves creating a simplified version of a product or service and using it to gather feedback and refine the design.
- Observation: Business analysts can observe stakeholders as they perform their work to understand their needs and requirements. Observation can be conducted in person or through the use of tools such as screen recording software.
Overall, the key to gathering requirements effectively is to ensure that the business analyst has a clear understanding of the needs and expectations of stakeholders and that those needs are documented in a way that is clear, concise, and actionable.
How business analysts do documentation
Documentation is an important part of the business analysis process, as it helps to ensure that the requirements and solutions developed by business analysts are clearly understood by all stakeholders.
There are several types of documentation that business analysts may create, including:
- Business Requirements Document (BRD): A BRD is a detailed document that outlines the business needs and expectations for a project. It typically includes information about the business problem or opportunity being addressed, the scope of the project, and the desired outcomes.
- Functional Requirements Document (FRD): An FRD is a detailed document that outlines the functional requirements for a project. It typically includes information about the specific features and functionality that will be included in the project, as well as any constraints or assumptions.
- Use Cases: A use case describes how a system or process will be used to achieve a specific goal. Use cases can be used to document the steps involved in completing a task and the expected outcomes.
- Process Maps: A process map is a visual representation of a business process, showing the steps involved and the flow of information and materials. Process maps can be used to document existing processes or to design new ones.
- Wireframes: A wireframe is a simplified visual representation of a user interface, showing the layout and functionality of a website or application. Wireframes can be used to document the design of a user interface and gather feedback from stakeholders.
Overall, the key to effective documentation is to ensure that it is clear, concise, and easy to understand and that it accurately reflects the requirements and solutions developed by the business analyst.
What do business analysts need to know?
Business analysts need to have a range of skills to be effective in their roles. Some of the key skills that business analysts need to know include:
- Data analysis: Business analysts need to be able to gather, analyze, and interpret data in order to understand business processes and identify problems.
- Problem-solving: Business analysts need to be able to identify problems and develop creative and effective solutions.
- Communication: Business analysts need to be able to communicate effectively with a wide range of stakeholders, including executives, managers, and subject matter experts.
- Documentation: Business analysts need to be able to document requirements and solutions in a clear and concise manner.
- Project management: Business analysts may be involved in managing projects or working with project managers, so it is important for them to have project management skills such as planning, budgeting, and risk management.
- Business acumen: Business analysts need to have a strong understanding of business concepts and principles in order to be able to analyze business processes and identify opportunities for improvement.
- Technical skills: Depending on the industry and the specific needs of the organization, business analysts may also need to have technical skills such as programming or data analysis.
Overall, business analysts need to have a broad range of skills.
how business analysts contribute technically to a project?
Business analysts can contribute technically to a project in a number of ways. Some of the ways in which business analysts may contribute technically to a project include:
- Data analysis: Business analysts can use data analysis techniques to understand business processes and identify problems. They may use tools such as spreadsheet software or specialized data analysis software to analyze data and extract insights.
- Process mapping: Business analysts can use process mapping techniques to document and understand business processes. They may use tools such as flowcharts or process modeling software to create visual representations of business processes.
- Prototyping: Business analysts can use prototyping techniques to test and refine ideas and solutions. They may use tools such as wireframing software or mockup tools to create simplified versions of a product or service and gather feedback from stakeholders.
- Testing: Business analysts may be involved in testing the functionality of a product or service to ensure that it meets the requirements and expectations of the business. They may use tools such as test cases or test plans to document and track testing activities.
Overall, business analysts can contribute technically to a project by using their analytical and technical skills to help understand and solve problems and by working with cross-functional teams to develop and implement solutions.
Business Analyst as a Career
Are business analysts in demand
Yes, business analysts are in high demand. Many companies and organizations rely on analysts to help them understand their operations, identify problems, and develop solutions. The demand for business analysts is expected to grow in the coming years as more and more organizations look to optimize their operations and improve their performance.
Are business analysts in demand in Canada
Delivery managers primary roles and responsibilities include:
- Planning and scheduling the delivery process, including defining project scope, milestones, and timelines.
- Managing the budget and resources of the delivery, including allocating tasks to team members and ensuring that the project stays on track.
- Identifying and managing risks to the delivery, including developing contingency plans to mitigate potential issues.
- Communicating with stakeholders, including team members, clients, and other stakeholders, to ensure that everyone is informed about the progress of the delivery.
- Tracking progress and making adjustments as needed to keep the delivery on track.
- Providing guidance and mentorship to team members to ensure that they have the skills and support they need to complete their tasks.
- Working with clients or other stakeholders to meet their needs and expectations.
Overall, delivery managers are responsible for ensuring that the delivery is completed on time, within budget, and to the required quality standards.
Business analyst for beginners
Yes, business analysts are in high demand in Canada. There are around 5000 BA jobs as of Jan 2023.
Are business analysts in demand in the U.K?
Yes, business analysts are in high demand in the U.K. There are around 10,000 BA jobs as of Jan 2023.

Are business analysts in demand in South Africa
Yes, business analysts are in high demand in the U.K. There are around 0,000 BA jobs as of Jan 2023.
What is the salary of a business analyst?
The salary of a business analyst can vary widely depending on a number of factors, including the industry, the size of the company, the location, the level of experience, and the specific responsibilities of the role.
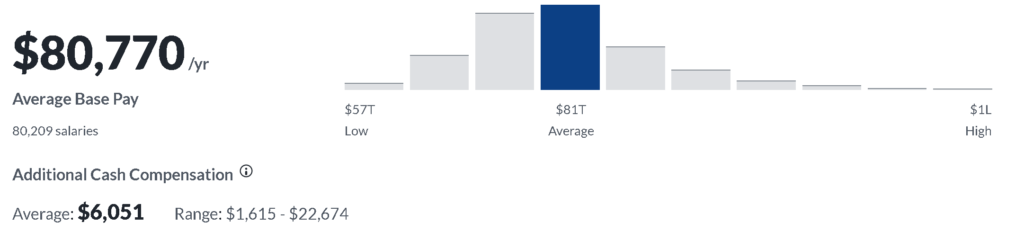
According to salary data from Glassdoor, the median salary for a business analyst in the United States is $74,532 per year. However, salaries for business analysts can range from $54,000 to $105,000 or more per year, depending on the factors mentioned above.
It’s worth noting that business analysts may also be eligible for bonuses, commissions, and other forms of compensation in addition to their base salary. In addition, business analysts can increase their earning potential through professional development and gaining additional skills and experience.
What is the salary of a business analyst in India?
The salary of a business analyst in India can vary widely depending on a number of factors, including the industry, the size of the company, the location, the level of experience, and the specific responsibilities of the role.
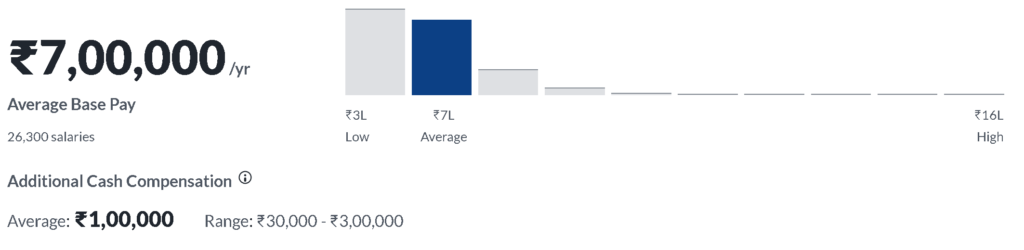
According to salary data from Glassdoor, the median salary for a business analyst in India is INR 7,00,000 per year. However, salaries for business analysts in India can range from INR 4,80,000 to INR 16,00,000 or more per year, depending on the abovementioned factors.
It’s worth noting that business analysts in India may also be eligible for bonuses, commissions, and other forms of compensation besides their base salary. In addition, business analysts in India can increase their earning potential through professional development and gaining additional skills and experience.
How is a business analyst as a career?
Business analysis can be a rewarding career for individuals who are analytical, detail-oriented, and enjoy problem-solving. Business analysts are professionals who analyze an organization or business domain (real or hypothetical) and document its business, processes, and systems. They use data to understand business processes, identify problems, and work with cross-functional teams to develop solutions.
Some of the benefits of a career in the business analysis include:
- Opportunities for growth and advancement: Business analysts often have the opportunity to progress to leadership roles or to specialize in a particular area of business analysis.
- Variety: Business analysts may work on a wide range of projects in different industries, which can provide opportunities to learn and grow.
- Impact: Business analysts play a key role in helping organizations to improve their processes, increase efficiency, and achieve their goals. This can be a satisfying aspect of the job for those who enjoy making a positive difference.
- Demand: Business analysts are in high demand, with the demand for their skills expected to continue to grow in the coming years.
Overall, a career in business analysis can be a fulfilling and rewarding choice for individuals who are interested in using their analytical skills to help organizations succeed.
Business Analyst Career transition to different roles
Why business analyst as a career?
Business analysis can be a rewarding career for analytical, detail-oriented individuals who enjoy problem-solving. Here are a few reasons why business analysis can be a great career choice:
- Opportunities for growth and advancement: Business analysts often have the chance to progress in leadership roles or to specialize in a particular area of business analysis.
- Variety: Business analysts may work on a wide range of projects in different industries, which can provide opportunities to learn and grow.
- Impact: Business analysts play a crucial role in helping organizations to improve their processes, increase efficiency, and achieve their goals. This can be a satisfying aspect of the job for those who enjoy making a positive difference.
- Demand: Business analysts are in high demand, with the demand for their skills expected to continue to grow in the coming years.
- Transferable skills: The skills that business analysts develop, such as data analysis, problem-solving, and communication, are valuable in a variety of industries and roles. Business analysts may have more flexibility in their career paths and may be able to transition to new roles or industries more easily.
Overall, a career in business analysis can be a fulfilling and rewarding choice for individuals who are interested in using their analytical skills to help organizations succeed.
The career path of a business analyst
The career path of a business analyst can vary depending on the individual’s goals and the opportunities available at their organization. Here are a few possible career paths for business analysts:
- Specialization: Some business analysts choose to specialize in a particular area, such as data analysis, project management, or a specific industry. By gaining expertise in a specific area, business analysts can increase their value to the organization and advance their careers.
- Leadership: Business analysts who excel in their roles may be promoted to leadership positions, such as team lead or manager. In these roles, business analysts may be responsible for managing and mentoring other business analysts, as well as setting goals and driving strategy.
- Consulting: Some business analysts may choose to move into consulting roles, where they can use their skills and expertise to help various organizations solve business problems.
- Entrepreneurship: Business analysts who are interested in starting their own businesses may choose to use their skills and experience to launch a startup or to consult on a freelance basis.
Overall, the career path of a business analyst will depend on the individual’s goals and the opportunities available to them. Business analysts who are proactive, take on new challenges, and continue to learn and grow will have the best chance of success in their careers.
Does a business analyst have a future?
Business analysts play a crucial role in helping organizations to understand their business processes, identify problems, and develop solutions. As such, the demand for business analysts is expected to continue to grow in the future.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, employment of business analysts is projected to grow 14% from 2019 to 2029, faster than the average for all occupations. This growth is driven by the increasing use of data and technology in business, as well as the need for organizations to become more efficient and competitive.
In addition to the growing demand for business analysts, the field is expected to evolve as new technologies and approaches emerge. Business analysts who can adapt to these changes and stay current with the latest trends and tools will be well-positioned for success in the future.
Overall, the future looks bright for business analysts, with solid demand and opportunities for growth and advancement.
Can a business analyst become a product manager?
Yes, business analysts can become product managers. Business analysts and product managers work to understand the needs of the business and use data to inform decision-making and drive the development of new products or services.
Business analysts often have a strong foundation in business analysis and are skilled at gathering and analyzing data to understand business processes and identify problems. They may also have experience working on cross-functional teams and be familiar with project management methodologies.
Product managers, on the other hand, are responsible for the strategy, roadmap, and execution of a product. They work closely with cross-functional teams to define and prioritize features, ensure that the product is delivered on time and to high quality, and measure and report on its success.
With the right experience and skills, business analysts can transition into product management roles. However, it is necessary to gain additional skills and expertise in product management methodologies, team leadership, and strategic thinking to make the transition successfully.
Can a business analyst become a data analyst?
Yes, business analysts can become data analysts. Business and data analysts are similar in some ways, but they also have some crucial differences.
Both business analysts and data analysts use data to help organizations make better decisions and improve their operations. They both work to understand the needs of the business and use data to identify problems, develop solutions, and measure the success of those solutions.
However, there are some critical differences between the two roles. Business analysts focus more on business, while data analysts focus more on the technical side. Business analysts often work with a wide range of data and use it to inform business decisions. In contrast, data analysts tend to focus more on specific data types and use them to answer particular questions.
With the right skills and experience, business analysts can transition into data analysis roles. However, it is necessary to gain additional skills and expertise in statistical analysis and data visualization to make the transition successfully.
Can a business analyst become a project manager?
Yes, business analysts can become project managers. Business analysts and project managers play essential roles in helping organizations improve their processes, increase efficiency, and achieve their goals.
Project managers are responsible for the planning, execution, and delivery of projects. They work with cross-functional teams to define project scope, set goals and objectives, create project plans, and manage resources to ensure that the project is delivered on time and to a high quality.
With the right experience and skills, business analysts can transition into project management roles. However, it is necessary to gain additional skills and expertise in project planning, risk management, and team leadership to make the transition successfully.
Can a business analyst become a developer?
Yes, business analysts can become developers. Business analysts and developers work to understand the needs of the business and use their skills and expertise to develop solutions to problems.
Developers design, build and maintain software systems. They use programming languages and tools to create and test code and work with cross-functional teams to ensure that the software meets the needs of the business.
With the right skills and experience, business analysts can transition into development roles. However, gaining additional skills and expertise in programming and software development may be necessary to make the transition successfully.
Can a business analyst become a consultant?
Yes, business analysts can become consultants. Business analysts and consultants work to help organizations understand their operations, identify problems, and develop solutions.
Consultants provide expert advice and support to organizations in a specific area of expertise. They work with clients to understand their needs, analyze their operations, and develop recommendations for improvement.
With the right skills and experience, business analysts can transition into consulting roles. However, gaining additional skills and expertise in business strategy and client relationship management may be necessary to make the transition successfully.
Can a business analyst become a product owner?
Yes, business analysts can become product owners. Business analysts and product owners work to understand the needs of the business and use data to inform decision-making and drive the development of new products or services.
Product owners are responsible for defining and prioritizing the features and functionality of a product. They work closely with development teams to ensure that the product meets the business’s and its customers’ needs and decide what should be built and when.
With the right skills and experience, it is possible for business analysts to transition into product owner roles. However, gaining additional skills and expertise in product management methodologies and agile development is necessary to make the transition successfully.
Will business analysts be replaced by AI?
Artificial intelligence (A.I.) and automation are changing how many industries operate, and the field of business analysis is no exception. While it is likely that A.I. and automation will continue to play a larger role in business analysis in the future, it is unlikely that business analysts will be replaced entirely by A.I.
A.I. and automation can be powerful tools for business analysts, helping them to analyze data faster and more accurately and to identify patterns and trends that might not be visible to the human eye. However, business analysts bring a unique set of skills and expertise to the table, including critical thinking, problem-solving, and the ability to communicate and work with people. These skills are difficult to replicate with A.I., and are likely to continue to be in high demand in the business analysis field.
The role of business analysts may evolve as A.I. and automation become more prevalent, but it is unlikely that BA will replace them entirely. Instead, business analysts will likely work alongside A.I. and automation to leverage their unique skills and expertise to help organizations succeed.
When is a business analyst brought into a project?
Business analysts are typically brought into a project when the project team needs to understand the business processes and requirements related to the project. This may be at the beginning of a project when the team is defining the scope and objectives or later in the project when the team is ready to start designing and building the solution.
Here are some specific situations when a business analyst may be brought into a project:
- To help define the scope and objectives of the project: Business analysts can help the project team understand the business needs and goals, and define the scope of the project in a way that aligns with those goals.
- To gather and analyze data: Business analysts can use data analysis and visualization tools to help the team understand business processes and identify problems or opportunities for improvement.
- To document requirements: Business analysts can work with stakeholders to gather and document the requirements for the project, including the business needs, functional requirements, and constraints.
- To design solutions: Business analysts can work with the project team to design solutions that meet the business needs and requirements.
- To test solutions: Business analysts may be involved in testing the functionality of a solution to ensure that it meets the requirements and expectations of the business.
Overall, business analysts are typically brought into a project when the project team needs help understanding and solving business problems.
Where business analysts work
Business analysts work in a wide range of industries and organizations, including:
- Financial services: Business analysts in the financial services industry may work for banks, investment firms, insurance companies, and other financial institutions. They may be involved in projects related to risk management, compliance, customer experience, and more.
- Healthcare: Business analysts in the healthcare industry may work for hospitals, clinics, insurance companies, and other healthcare organizations. They may be involved in projects related to electronic health records, patient care, billing, and more.
- Technology: Business analysts in the technology industry may work for software companies, hardware manufacturers, and other organizations that develop and sell technology products and services. They may be involved in projects related to software development, data analysis, and more.
- Manufacturing: Business analysts in the manufacturing industry may work for companies that produce goods, such as consumer products, automotive parts, and industrial equipment. They may be involved in projects related to supply chain management, process improvement, and more.
- Government: Business analysts may work for government agencies at the local, state, or federal level. They may be involved in projects related to policy, budgeting, and more.
Overall, business analysts can work in a wide range of industries and organizations, and their specific responsibilities will depend on the needs of the organization and the specific project they are working on.
How to get a job as a business analyst?
Here are a few steps you can take to increase your chances of getting a job as a business analyst:
- Earn a relevant degree: While a degree is not always required for a business analyst position, it can be helpful to have a bachelor’s degree in a field such as business, finance, computer science, or another related field.
- Gain relevant experience: Many business analyst positions require some level of experience, so it can be helpful to gain experience through internships, part-time jobs, or volunteer work in a business or technical role.
- Get certified: There are a number of certification programs available for business analysts, such as the Certified Business Analysis Professional (CBAP) from the International Institute of Business Analysis (IIBA). Earning a certification can help to demonstrate your knowledge and skills to potential employers.
- Build a strong resume: A strong resume that highlights your relevant education, experience, and skills can help you stand out to potential employers.
- Network: Networking can be a valuable way to learn about job openings and to make connections in the business analysis field. Consider joining professional organizations, attending industry events, and connecting with other business analysts on LinkedIn.
- Tailor your job search: When searching for business analyst jobs, make sure to tailor your resume and cover letter to the specific requirements of the position. This can show potential employers that you are a good fit for the role.
Overall, you can take several steps to increase your chances of getting a job as a business analyst. By building your skills, gaining relevant experience, and networking effectively, you can increase your chances of finding the right job in the field.
is business analyst a stressful job
Like any job, business analysis can have its stressors and challenges. However, the level of stress can vary depending on a variety of factors, such as the specific project, the organizational culture, and the individual’s ability to manage their workload and stress.
Here are a few common stressors that business analysts may encounter:
- Tight deadlines: Business analysts may be under pressure to complete projects on tight deadlines, which can be stressful.
- Managing stakeholders: Business analysts may have to work with a wide range of stakeholders, including executives, managers, and subject matter experts. Managing these relationships and effectively communicating with these stakeholders can be challenging.
- Complex projects: Business analysts may work on projects that are complex and require a high level of attention to detail. This can be stressful, especially if the stakes are high or the project is particularly large or important.
- Changing requirements: Business analysts may need to adapt to changing requirements or priorities as a project progresses, which can be stressful.
Overall, business analysis can be a challenging and rewarding career, but like any job, it can have its stressors. It is important for business analysts to be able to manage their workload and stress effectively in order to be successful in their roles.
does business analyst require coding?
The extent to which a business analyst is expected to know coding will depend on the specific role and the needs of the organization.
In some cases, a business analyst may be expected to have some coding skills in order to be able to work with technical teams and understand how code is used to implement business solutions. For example, a business analyst working on a software development project may need to understand how to write simple scripts or queries in order to test and validate solutions.
In other cases, a business analyst may not be expected to have coding skills, but may work with developers or other technical team members who handle the coding. In these cases, the business analyst may focus more on the business and functional aspects of the project, such as gathering requirements and designing solutions.
business analyst for freshers
If you are a fresher (new graduate) interested in starting a career as a business analyst, there are a few key things you can do to increase your chances of success:
- Earn a relevant degree: While a degree is not always required for a business analyst position, it can be helpful to have a bachelor’s degree in a field such as business, finance, computer science, or another related field.
- Gain relevant experience: Many business analyst positions require some level of experience, so it can be helpful to gain experience through internships, part-time jobs, or volunteer work in a business or technical role. This can help you to build your skills and to gain practical experience that will be valuable in your future career.
- Get certified: There are a number of certification programs available for business analysts, such as the Certified Business Analysis Professional (CBAP) from the International Institute of Business Analysis (IIBA). Earning a certification can help to demonstrate your knowledge and skills to potential employers.
- Build a strong resume: A strong resume that highlights your education, experience, and skills can help you stand out to potential employers. Be sure to emphasize any relevant coursework or projects you completed as part of your degree program.
- Network: Networking can be a valuable way to learn about job openings and to make connections in the business analysis field. Consider joining professional organizations, attending industry events, and connecting with other business analysts on LinkedIn.
Overall, there are a number of steps you can take as a fresher to increase your chances of starting a successful career as a business analyst. By building your skills, gaining relevant experience, and networking effectively, you can increase your chances of finding the right job in the field.
Business analysis can be a rewarding career choice in India for individuals who are analytical, detail-oriented, and enjoy problem-solving.
The demand for business analysts is strong in India, driven by the increasing use of data and technology in business, as well as the need for organizations to become more efficient and competitive.
According to a survey by the International Institute of Business Analysis (IIBA), the demand for business analysts in India is expected to continue to grow in the coming years.
business analyst as a career in India
Comparison of Business Analyst with other profiles
Business analyst versus data analyst
Business analysts and data analysts are similar in that they both work with data and use analytical skills to solve business problems. However, there are some key differences between the two roles:
- Scope of work: Business analysts focus on the overall business and its processes, while data analysts focus specifically on data and statistical analysis.
- Stakeholder engagement: Business analysts may work more closely with stakeholders, such as executives, managers, and subject matter experts, to understand the business needs and goals and to develop solutions. Data analysts may work more with technical teams and may be more focused on the technical aspects of data analysis.
- Types of problems: Business analysts may be called upon to solve a wide range of business problems, from identifying inefficiencies in business processes to developing new products or services. Data analysts, on the other hand, may be more focused on analyzing data to answer specific questions or to inform decision-making.
- Skillset: Business analysts may need a broader range of skills, including communication, stakeholder management, and process improvement. Data analysts may need more specialized technical skills, such as coding and statistical analysis.
Overall, business analysts and data analysts both play important roles in helping organizations to understand and solve problems, but the scope of their work and the skills they bring to the table can be quite different.
Business analyst versus product owner
Business analysts and product owners are both involved in the development and management of products, but they have different roles and responsibilities.
Product owners, on the other hand, are responsible for defining the vision and strategy for a product and for prioritizing the features and capabilities that will be included in the product. They work closely with development teams to ensure that the product is delivered on time and meets the needs of the business.
Here are a few key differences between business analysts and product owners:
- Scope of work: Business analysts may focus on specific projects or processes within an organization, while product owners are responsible for the overall direction and strategy of a product.
- Stakeholder engagement: Business analysts may work more closely with stakeholders, such as executives, managers, and subject matter experts, to understand the business needs and goals and to develop solutions. Product owners may work more with development teams and may be more focused on the technical aspects of product development.
- Decision-making authority: Business analysts may have less decision-making authority than product owners, who are responsible for defining the vision and strategy for a product and for prioritizing the features and capabilities that will be included in the product.
Overall, business analysts and product owners are both important roles in the development and management of products, but they have different responsibilities and focus areas.
business analyst versus project manager
A business analyst is a professional who focuses on analyzing and improving business processes. They identify problems and opportunities and then work with the stakeholders to find solutions that align with the company’s goals. They may also create documentation, such as business requirements or user stories, and communicate with various teams to ensure that projects are completed on time and within budget.
A project manager is responsible for planning, organizing, and managing resources to complete specific project goals and objectives successfully. They are typically accountable for the overall direction, coordination, implementation, execution, control, and completion of a project, as well as the management of the project team. Project managers may also be responsible for budgeting, resource allocation, stakeholder communication, and risk management.
Generally, business analysts focus more on analyzing and improving business processes, while project managers focus on planning and executing projects. However, the roles can overlap, and a single individual may perform both tasks.
business analyst versus product manager
A business analyst is a professional who focuses on analyzing and improving business processes. They identify problems and opportunities and then work with the stakeholders to find solutions that align with the company’s goals. They may also create documentation, such as business requirements or user stories, and communicate with various teams to ensure that projects are completed on time and within budget.
A product manager is responsible for developing and succeeding in a specific product or product line. They work with cross-functional teams to define, design, and deliver new products and improve existing ones. Product managers are responsible for the entire lifecycle of a product, from ideation and market research to launch and beyond. They may also set the product roadmap and manage the product budget.
In general, business analysts focus more on analyzing and improving business processes, while product managers focus on developing and managing specific products. However, the roles can overlap, and a single individual may perform both tasks.
business analyst vs. data scientist
Business analysts and data scientists are professionals who work with data but have different areas of focus and responsibilities.
Data scientists focus on analyzing and interpreting complex data sets to extract valuable insights and solve complex problems. They use various tools and techniques, such as machine learning, to analyze and interpret data and communicate their findings to stakeholders clearly and understandably. Data scientists may also be responsible for developing algorithms and predictive models to support decision-making and drive business growth.
In general, business analysts focus more on improving business processes, while data scientists focus on analyzing and interpreting data to extract insights and solve complex problems. However, the roles can overlap, and a single individual may perform both tasks.
business analyst vs. software developer
Business analysts and software developers are professionals who work with technology but have different areas of focus and responsibilities.
Business analysts are focused on analyzing and improving business processes. They use data to identify problems and opportunities and then work with stakeholders to find solutions that align with the company’s goals. Business analysts may also create documentation, such as business requirements or user stories, and communicate with various teams to ensure that projects are completed on time and within budget.
Software developers are responsible for designing, developing, and maintaining software systems. They use programming languages to write and test code and then work with cross-functional teams to ensure that the software is delivered on time and meets the required specifications. Software developers may also be responsible for debugging code, troubleshooting issues, and updating and maintaining existing software systems.
In general, business analysts focus more on analyzing and improving business processes, while software developers focus on designing and building software systems. However, the roles can overlap, and a single individual may perform both tasks.








